#populate attributes with UMAP for plotting
#you can use the optional argument npc to select more or less PCs
myobj <- ruUMAP(myobj)[1] "Altering UMAP configurations..."
[1] "Running UMAP..."
[1] "Saving custom configuration..."Kaitlin Sullivan
The following video tutorial demonstrates the functionality of ruUMAP() and ruCluster(), two functions that dimensionally reduce and hierarchically (method = “ward.D2”) cluster the data.
Note that UMAPs have built-in stochasticity, meaning they will look different between computers
Follow along with the code below.
ruUMAP()Once run, you can access the UMAP coordinates in the attributes (@attributes$umap).
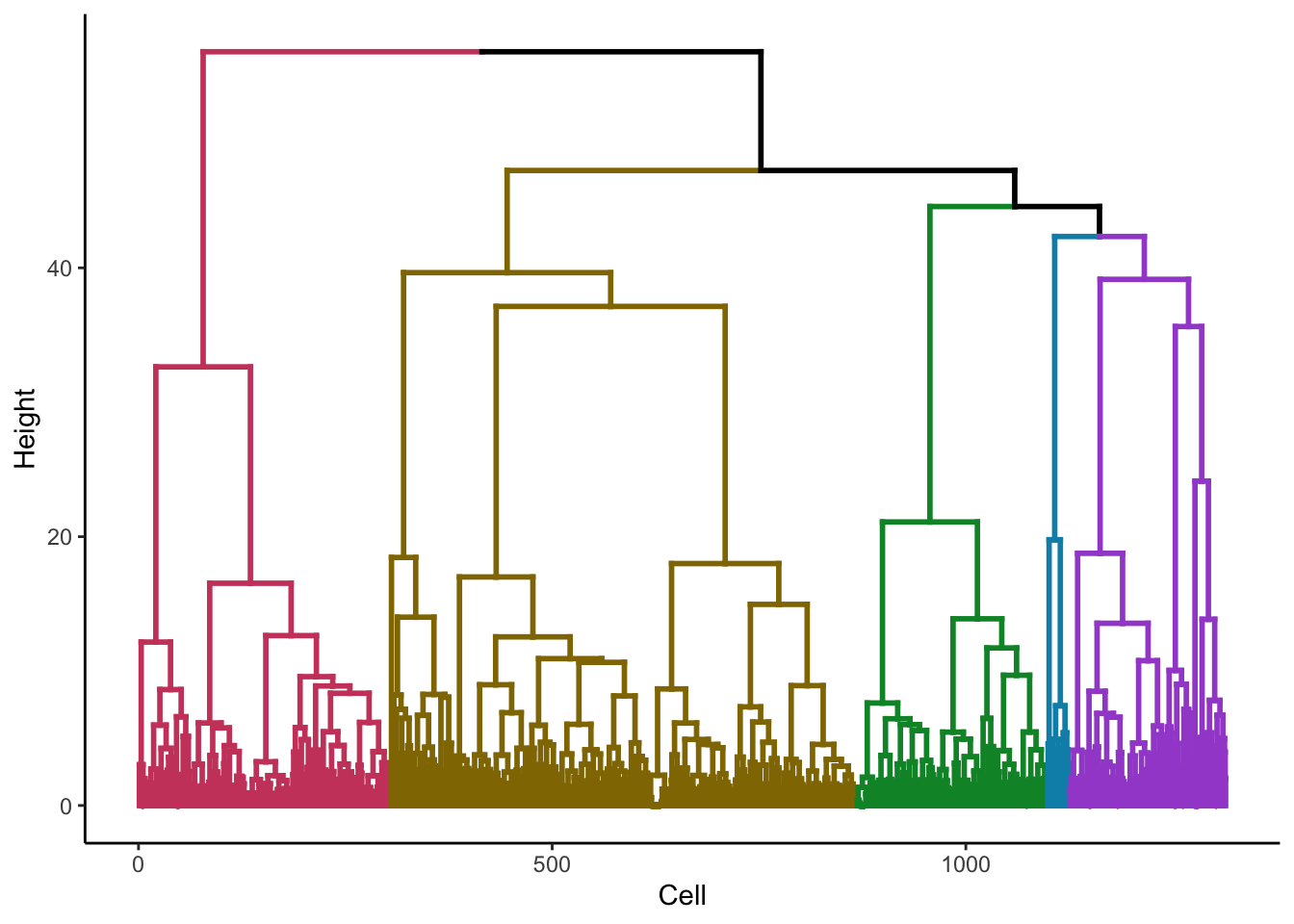
ruCluster()This function clusters the data using ward D2 hierarchical clustering. Select a number of clusters you beleive the data might have. Once run, a new @metaData column will be generated.
To refine the number of clusters, check the dendrogram with plotDendro() and re-run ruCluster() as many times as you see fit.
[1] "Clustering..."[1] "Creating dendrogram..."
[1] "Plotting..."
[1] "Please wait, this may take a while..."